Realtime Classification
Contents
Realtime Classification#
Let say you want to cut your realtime recording audio by using VAD after that classify using classification models, you can do that with Malaya-Speech!
This tutorial is available as an IPython notebook at malaya-speech/example/realtime-classification.
This module is language independent, so it save to use on different languages. Pretrained models trained on multilanguages.
This is an application of malaya-speech Pipeline, read more about malaya-speech Pipeline at malaya-speech/example/pipeline.
[1]:
import malaya_speech
from malaya_speech import Pipeline
Load VAD model#
Fastest and common model people use, is webrtc. Read more about VAD at https://malaya-speech.readthedocs.io/en/latest/load-vad.html
[2]:
webrtc = malaya_speech.vad.webrtc()
Recording interface#
So, to start recording audio including realtime VAD and Classification, we need to use malaya_speech.streaming.record. We use pyaudio library as the backend.
def record(
vad,
asr_model = None,
classification_model = None,
device = None,
input_rate: int = 16000,
sample_rate: int = 16000,
blocks_per_second: int = 50,
padding_ms: int = 300,
ratio: float = 0.75,
min_length: float = 0.1,
filename: str = None,
spinner: bool = False,
):
"""
Record an audio using pyaudio library. This record interface required a VAD model.
Parameters
----------
vad: object
vad model / pipeline.
asr_model: object
ASR model / pipeline, will transcribe each subsamples realtime.
classification_model: object
classification pipeline, will classify each subsamples realtime.
device: None
`device` parameter for pyaudio, check available devices from `sounddevice.query_devices()`.
input_rate: int, optional (default = 16000)
sample rate from input device, this will auto resampling.
sample_rate: int, optional (default = 16000)
output sample rate.
blocks_per_second: int, optional (default = 50)
size of frame returned from pyaudio, frame size = sample rate / (blocks_per_second / 2).
50 is good for WebRTC, 30 or less is good for Malaya Speech VAD.
padding_ms: int, optional (default = 300)
size of queue to store frames, size = padding_ms // (1000 * blocks_per_second // sample_rate)
ratio: float, optional (default = 0.75)
if 75% of the queue is positive, assumed it is a voice activity.
min_length: float, optional (default=0.1)
minimum length (s) to accept a subsample.
filename: str, optional (default=None)
if None, will auto generate name based on timestamp.
spinner: bool, optional (default=False)
if True, will use spinner object from halo library.
Returns
-------
result : [filename, samples]
"""
pyaudio will returned int16 bytes, so we need to change to numpy array, normalize it to -1 and +1 floating point.
Check available devices#
[3]:
import sounddevice
sounddevice.query_devices()
[3]:
> 0 MacBook Pro Microphone, Core Audio (1 in, 0 out)
< 1 MacBook Pro Speakers, Core Audio (0 in, 2 out)
2 JustStream Audio Driver, Core Audio (2 in, 2 out)
By default it will use 0 index.
Load Classification models#
In this example, I am going to use 3 different modules, gender detection, language detection and age detection.
[4]:
gender_model = malaya_speech.gender.deep_model(model = 'vggvox-v2')
language_detection_model = malaya_speech.language_detection.deep_model(model = 'vggvox-v2')
age_model = malaya_speech.age_detection.deep_model(model = 'vggvox-v2')
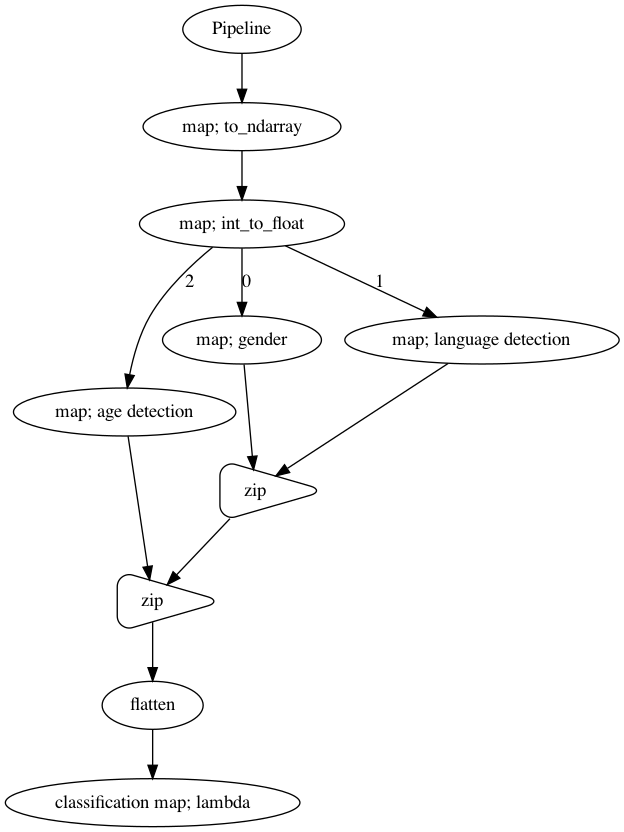
Classification Pipeline#
Because pyaudio will returned int16 bytes, so we need to change to numpy array then normalize to float, feel free to add speech enhancement or any function, but in this example, I just keep it simple. And needs to end with ``classification`` map or else ``malaya_speech.streaming.record`` will throw an error.
[5]:
p_classification = Pipeline()
to_float = p_classification.map(malaya_speech.astype.to_ndarray).map(malaya_speech.astype.int_to_float)
gender = to_float.map(gender_model)
language_detection = to_float.map(language_detection_model)
age_detection = to_float.map(age_model)
combined = gender.zip(language_detection).zip(age_detection).flatten()
combined.map(lambda x: x, name = 'classification')
p_classification.visualize()
[5]:
Again, once you start to run the code below, it will straight away recording your voice.
If you run in jupyter notebook, press button stop up there to stop recording, if in terminal, press CTRL + c.
[6]:
file, samples = malaya_speech.streaming.record(webrtc, classification_model = p_classification)
Listening (ctrl-C to stop recording) ...
Sample 0 2021-05-31 23:39:19.638932: ['male', 'not a language', 'not an age']
Sample 1 2021-05-31 23:39:19.874754: ['male', 'malay', 'teens']
Sample 2 2021-05-31 23:39:21.262149: ['not a gender', 'not a language', 'not an age']
Sample 3 2021-05-31 23:39:23.363767: ['not a gender', 'not a language', 'not an age']
Sample 4 2021-05-31 23:39:28.221167: ['male', 'not a language', 'teens']
Sample 5 2021-05-31 23:39:31.076877: ['male', 'malay', 'teens']
Sample 6 2021-05-31 23:39:35.456165: ['male', 'not a language', 'teens']
Sample 7 2021-05-31 23:39:38.438468: ['male', 'not a language', 'teens']
Sample 8 2021-05-31 23:39:40.711461: ['male', 'not a language', 'teens']
saved audio to savewav_2021-05-31_23-39-42_725496.wav
[7]:
import IPython.display as ipd
ipd.Audio(file)
[7]:
[8]:
len(samples)
[8]:
9
[9]:
type(samples[0][0]), samples[0][1]
[9]:
(bytearray, ['male', 'not a language', 'not an age'])
